for Your Well-Being
for Your Well-Being
Otology is a highly specialised branch of ENT that focuses on medical and surgical treatments of the ear, hearing and balance.
Otology is a highly specialised branch of ENT that focuses on medical and surgical treatments of the ear, hearing and balance.
Hearing loss
Diminished ability to hear sound, temporarily or permanently, when any part of the hearing system (outer ear, middle ear, inner ear, or auditory nerve) is damaged. It can affect children’s speech and learning and, in adults, is linked to conditions such as depression and dementia.
Sudden sensorineural hearing loss (SSHL) or sudden deafness
Rapid, unexplained loss of hearing. It typically affects only one ear and is considered a medical emergency, requiring immediate attention (it needs to be seen within 72 hours of onset) to improve the chances of recovery.
Hearing loss in one ear
Also known as unilateral hearing loss or single-sided deafness, it is the complete or significant inability to hear in one ear while the other ear retains normal or partial hearing ability.
Canal dehiscence syndrome (SSCD):
A rare condition caused by a tiny hole in the bone covering the inner ear’s balance canal, which can lead to symptoms such as vertigo, imbalance, hearing difficulties, autophony (hearing internal sounds abnormally loud, such as your voice, your pulse or your eyes moving), and tinnitus.
Tympanic membrane (eardrum) perforation
A hole in the eardrum caused by infections, sudden pressure changes (from a flight or diving) or trauma to the ear. It can make the ear susceptible to infections and result in hearing loss. The membrane may heal over time, though surgery is sometimes needed to close the perforation.
Tympanic membrane (eardrum) retraction
Occurs when the eardrum is pulled inward due to negative pressure in the middle ear or scarring. It can lead to complications such as hearing loss, infections, or damage to the ear’s delicate structures.
Recurrent ear infections
Defined as three episodes in six months or four in a year. Causes include genetics, smoke exposure, respiratory infections, or eustachian tube issues. Left untreated, they may lead to hearing loss, speech delays, or chronic inflammation.
Cholesteatoma
Develops when trapped skin forms a mass in the ear. It causes harm if untreated as it may destroy the bones in the middle ear or spread to nearby areas. Symptoms include hearing loss, ear discharge, facial weakness and vertigo. Surgical intervention is usually required to remove the disease and prevent further damage.
Otosclerosis
An inherited disease where abnormal bone growth creates an obstruction around the stapes bone in the middle ear and inhibits sound transmission to the inner ear. It causes hearing loss, which worsens gradually and can occur in one or both ears. Hearing aids can help to amplify sound. Surgery (stapedotomy) can restore hearing by bypassing the obstruction using a tiny prosthetic piston to conduct sound to the inner ear.
Obstructive Eustachian tube dysfunction
If the Eustachian tube is not opening correctly, you may feel fullness in the ear, pressure and/or pain in the ear, and muffled hearing. Common causes are allergies, colds, or sinus infections. Treatment may include nasal medications, Eustachian tube balloon dilatation or ventilation tubes (grommets).
Patulous Eustachian tube
Occurs when the Eustachian tube stays abnormally open, leading to symptoms like autophony (hearing internal sounds abnormally loud, such as your own voice or breathing), ear fullness, and tinnitus. The symptoms may come and go, change with posture and get worse with exercise. Causes can include weight loss and hormonal shifts.
Meniere’s disease
Causes episodes of vertigo, tinnitus, pressure or fullness in the ear and fluctuating hearing loss. The exact reason for this is unknown, but it’s linked to a fluid build-up in the inner ear. Symptom management involves dietary changes, medication, intratympanic injections and sometimes surgical interventions.
Glue ear (otitis media with effusion)
Fluid behind the eardrum. It often occurs after a cold and may affect one or both ears. The main symptom of glue ear is hearing loss. Some children with glue ear may get recurrent ear infections or delays in speech and language development. Treatment ranges from monitoring to medication or ventilation tube insertion.
Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (BPPV)
A common condition where specific head movements can cause dizziness, such as turning over in bed. It is caused by displaced crystals in the inner ear. In most cases, this can be effectively treated with the Epley Manoeuvre and other manoeuvres to reposition the particles.
Vestibular neuronitis and labyrinthitis
Are similar conditions caused by inflammation or infection of the vestibular (balance) nerve and inner ear, respectively. Labyrinthitis may cause hearing loss and tinnitus as well as vertigo and imbalance.
Exostoses (Surfer’s Ear):
Benign bony growths in the ear canal caused by repeated exposure to cold water and wind. These growths can narrow the ear canal, leading to issues like water trapping, infections, and hearing difficulties.
Sudden sensorineural hearing loss (SSNHL) or sudden deafness
Rapid, unexplained hearing loss that occurs suddenly or over hours to days. It is often perceived as a ‘blocked’ ear when using headphones or the phone. Some people notice it when they wake up in the morning. It typically affects only one ear and is considered a medical emergency requiring immediate attention (within 72 hours of onset) to improve chances of recovery.
Recurrent ear infections
Repeated episodes of ear discharge and/or pain. This could be due to an outer or middle ear infection. Recurring ear infections, especially if painless, may also indicate an underlying problem with the eardrum or ear canal, leading to more serious consequences if not addressed promptly.
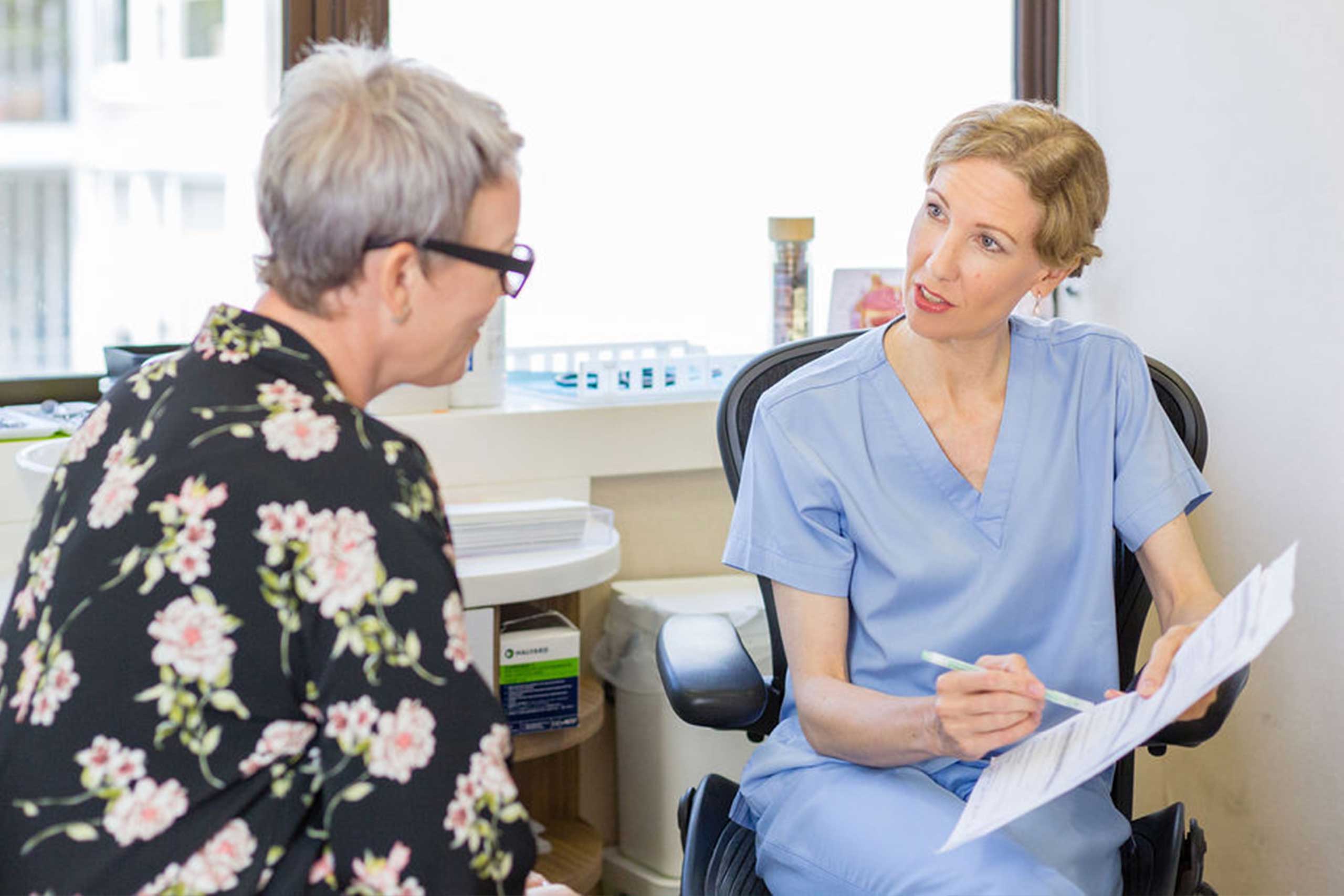

Visiting an otologist (ear and hearing specialist) is the first step to maintaining or enhancing your ear and hearing health.
Seek medical help from an Otologist if you are suffering from:
Dr Rebecca Heywood provides a variety of treatments to address your specific needs. If you do not see your ear or hearing concern listed, please feel free to reach out for personalised assistance.
Intratympanic (in the ear) steroid injection
Injection of steroid medicine through the eardrum into the middle ear space.
Tympanoplasty / Myringoplasty
Surgery to repair a perforated or retracted eardrum and any associated damage to the hearing bones in the middle ear.
Ossiculoplasty
Surgery to repair or replace the hearing bones in the middle ear.
Stapedectomy / stapedotomy
Surgery to remove part of the stapes bone and replace it with a prosthesis.
Cochlear implantation
Surgical implantation of a device to restore hearing to those who struggle to hear with a conventional hearing aid.
Bone conduction implantation
Surgical implantation of a device to conduct sound directly to the inner ear using bone conduction
Middle ear implantation
Surgical implantation of a device to improve hearing by directly stimulating the middle ear hearing bones.
Tympanomastoidectomy
Removes chronic infection or cholesteatoma from the middle ear and mastoid air cells.
Blind Sac closure
Surgery to close the ear canal in cases of severe ear disease.
Canaloplasty
Surgery to widen the ear canal.
Meatoplasty
Surgery to enlarge the ear canal opening.
Mastoid cavity obliteration
Procedure to fill the mastoid cavity to prevent chronic ear drainage.
Semicircular canal dehiscence surgery
To close a defect in an affected balance canal of the inner ear to bring relief from hearing and balance symptoms.
Balloon Eustachian tuboplasty
Procedure performed to help the Eustachian tube open more easily by dilating it with a small balloon.
Myringotomy & grommet insertion
Procedure involving a small incision in the eardrum to drain fluid and insert a ventilation tube (grommet) to ventilate the middle ear and prevent further build-up of fluid.
Dr Rebecca provides personalised care that is both empathetic and expertly delivered. With a reputation for precision and a deep understanding of each patient’s unique needs, she empowers individuals at every step of their treatment journey. Having performed surgeries across the globe and led progressive research on the link between hearing loss and dementia, Dr Rebecca is recognised for her knowledge and contributions to the medical field.
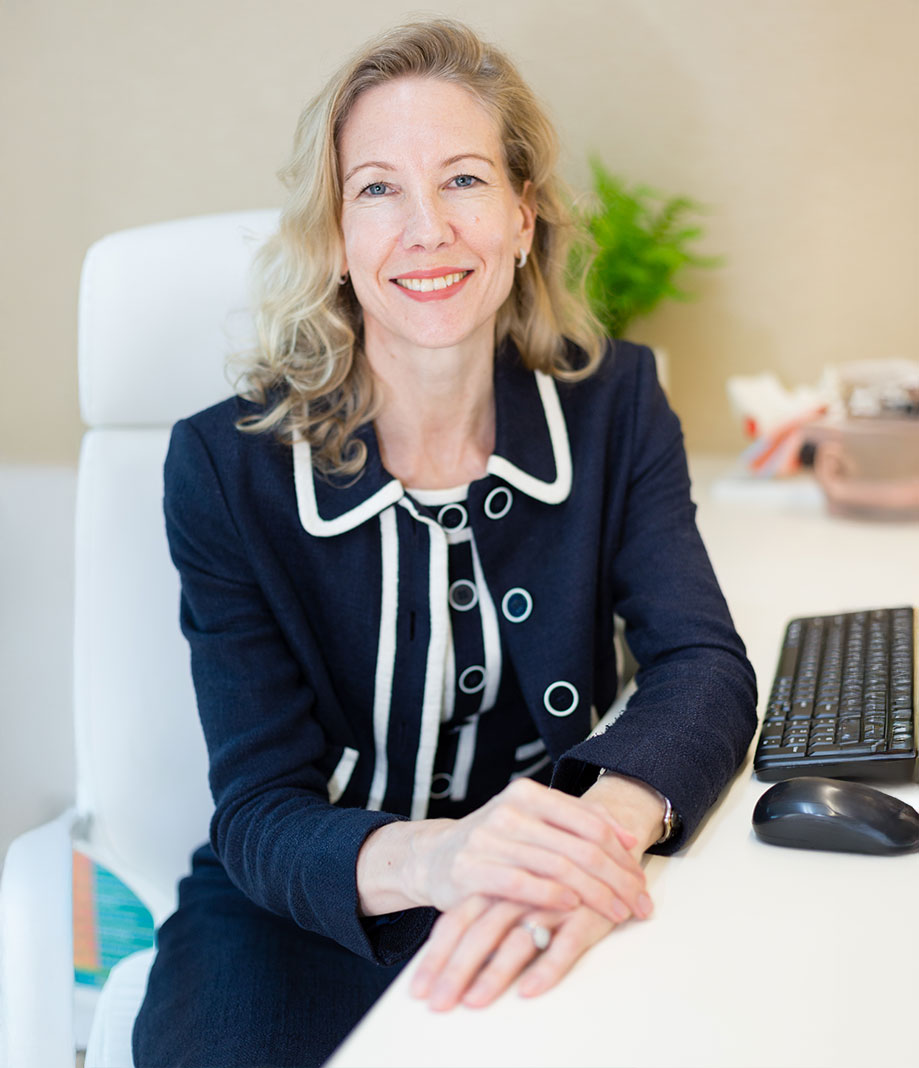


Dr Rebecca Heywood is a fully accredited Ear and Hearing Surgeon in Singapore focused on transforming patients’ lives through her expert ENT medical services. Known for her skills and accreditations in Otology & Neurotology, she focuses on providing bespoke solutions for disorders that affect the ear, hearing and balance.
Gleneagles Hospital
6A Napier Road #03-41/42
Gleneagles Annexe Block
Singapore 258500
Camden Medical Centre
1 Orchard Boulevard #12-09
Singapore 248649
©2025 All Rights Reserved. Website Created by No.23 Collective.